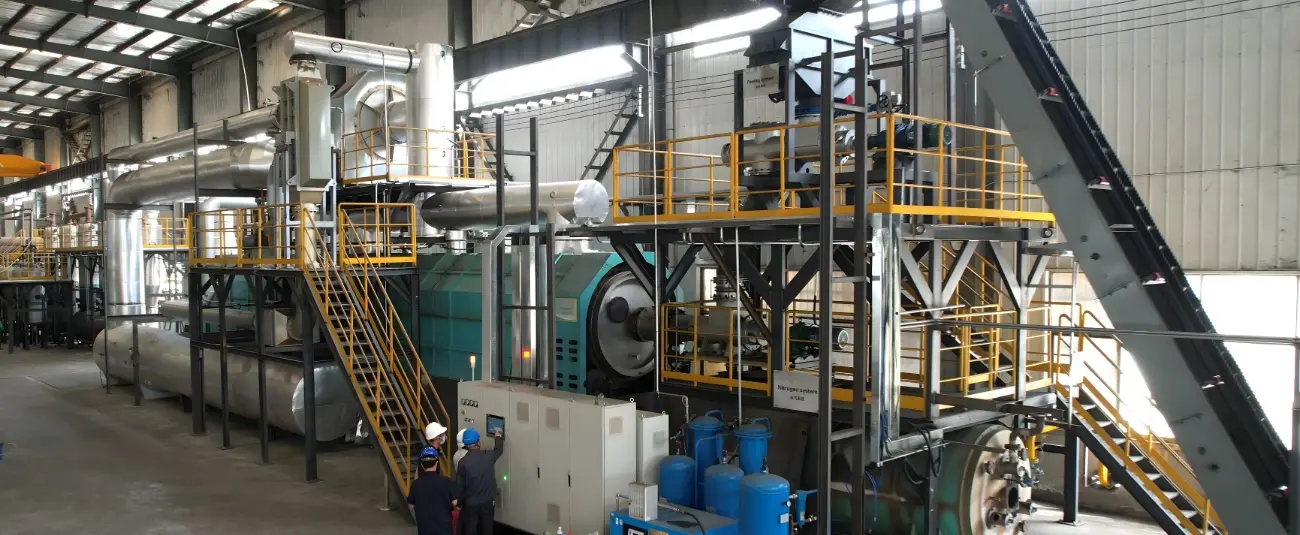
The global shift toward low-carbon energy systems has intensified the demand for sustainable biomass conversion technologies. Charcoal production, long associated with traditional energy use, is undergoing a technological renaissance. Modern charcoal making machines enable controlled carbonization of organic materials, transforming agricultural residues, wood, and other biomass into biochar and energy-dense charcoal. This transition from conventional firewood to engineered charcoal is central to decarbonizing rural and industrial energy systems while generating ancillary environmental benefits.
Advancing Carbon Sequestration through Biochar
One of the most compelling contributions of biochar machine for sale is their capacity to produce biochar, a stable form of carbon capable of long-term sequestration. When applied to soils, biochar enhances nutrient retention, reduces greenhouse gas emissions from decomposition, and contributes to a measurable reduction in atmospheric carbon. Modern biochar machines for sale are designed to optimize pyrolysis temperatures and residence times, ensuring maximum carbon retention while producing minimal pollutants. The adoption of such machines positions biomass utilization as a climate-positive energy strategy rather than a mere fuel source.
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
Charcoal making machines can be integrated into broader renewable energy systems, providing a versatile energy vector. The pyrolysis gas generated during carbonization can be captured and used to fuel boilers, generators, or combined heat and power systems, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This dual-purpose functionality exemplifies how biomass conversion can simultaneously supply thermal energy, electricity, and soil amendments, aligning with low-carbon energy frameworks. Deploying biochar machines for sale in communities with abundant biomass waste thus enables distributed, carbon-conscious energy production.
Mitigating Environmental Pollution
Traditional charcoal production methods are often inefficient and highly polluting, releasing particulate matter and volatile organic compounds. Modern charcoal making machines mitigate these issues through enclosed carbonization chambers, automated feeding systems, and gas scrubbing mechanisms. These innovations minimize emissions, enhance energy efficiency, and allow precise control over carbonization kinetics. The ability to monitor and regulate temperature and airflow ensures that the resulting charcoal and biochar meet environmental standards, making these machines indispensable in sustainable energy planning.
Economic and Societal Impacts
The deployment of charcoal making machines has significant socio-economic implications. By valorizing agricultural residues and wood waste, operators can generate a marketable commodity while reducing deforestation pressure. The sale of biochar provides additional revenue streams, incentivizing sustainable land management and local energy resilience. Accessible biochar machines for sale facilitate small-scale adoption, enabling rural enterprises to participate in low-carbon energy transitions while enhancing local livelihoods.
Strategic Role in Global Energy Transitions
Charcoal making machines are not merely tools for energy production; they are strategic instruments in global low-carbon transitions. By converting waste biomass into stable carbon, energy, and soil amendments, they support multiple environmental and economic objectives simultaneously. Their proliferation demonstrates that low-carbon energy solutions can be decentralized, economically viable, and ecologically restorative, offering a tangible pathway toward meeting international climate targets.
The combination of emission reduction, energy recovery, and carbon sequestration underscores the pivotal role of charcoal making machines in shaping sustainable, low-carbon energy futures.